Example of RF amplifier for DAB
Interesting ? Yes but... before thinking to use this kind of gizmo after the USRP, the RF signal need some manipulations, avoiding any disturbance on the radio spectrum.
NEVER CONNECT TO AN ANTENNA WITHOUT A LICENSE !
Output Spectrum
Usually when somebody need to transmit easily voices information on the radio spectrum he use an oscillator directly modulated and tuned on the working frequency. To avoid unwanted signals outside the working band (harmonics) low pass filters are mainly used after this oscillator and amplifiers.
It is also possible to use RF mixer to up convert the frequency from the modulated oscillator on a higher band when intermediate line is used to carry the RF signal from the modulator stage to the up-converter / power amplifier. (This mainly used on Terrestrial link, Uplink Earth Station, Vsat terminals) This allow also frequency agility on a larger band. In this case a mix of high pass and low pass or bandpass filters are used to keep the energy where it should be !
USRP boards propose different band coverage and use direct output from the DA or converted RF spectrum. As we use digital modulation (OFDM in this case... including amplitude modulation) we need also a good linearity on the RF chain to avoid distortion. The amplifiers will not work near their saturation point but where we get the best linearity. (I & Q frame are send from the PC to the USRP FPGA, after computing, signal is applied to DA's to generate the modulation. In the case of RF mixing for band conversion we should also ensure that we do not introduce too much additional phase noise (mainly from the up-converter local oscillator)
Basic TX
Test with the BasicTX, On the picture you see the board installed on the USRP TX A port (Upper right) This board take the signal from the DA's and provide the output on SMA connectors via a transformer. The don't use any actives components, you get after the transformer what you get directly from the DA. When we generate a signal on this board we have measured a total power of 18 uW. (with 50 ohm load 0 dB of gain on the gnuradio module)
As we use one DA from the TX A port we get a real signal at the output, meaning that you get every harmonics and image frequency till they go in the noise floor (bandwidth of the board transformer)
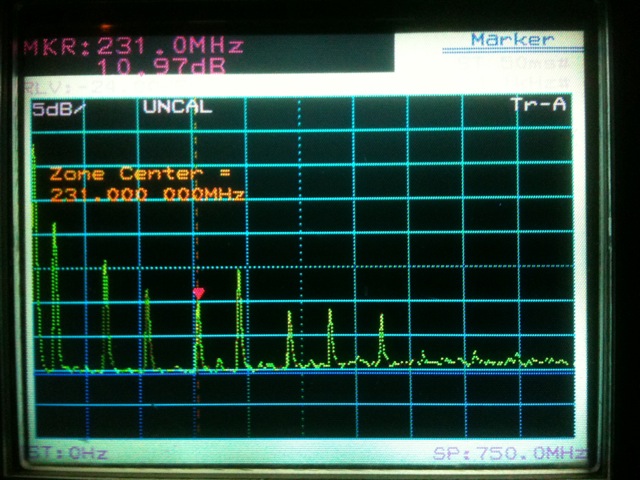
This is typically how looks the output of the BasicTX when you analyze the spectrum. Note the red marker showing the desired working frequency in the Band III (exact value: 12C @227.360 Mhz during the measurement).
To filter the lower and stronger peaks will required more than 80 dB of attenuation and the same for the next upper peak ! The picture show the spectrum from 0 to 750 Mhz
So ! this will required further filtering before applying any pre amplifier stage... tbc
RFX400
The RFX400 can work from 400Mhz to 500 Mhz with a total power up to 200 mW. To use it on the bandIII on the channels 10,11,12 we need to make some modification.
The conversion is done with a quadrature modulator (AD8345) taking the two DAC's signal and a carrier from a programmable local oscillator (PLL using one ADF4360). The card include also for the TX path 2 stages of amplification before a low pass filter. The bandwidth of the last stage will not go under 300 Mhz.
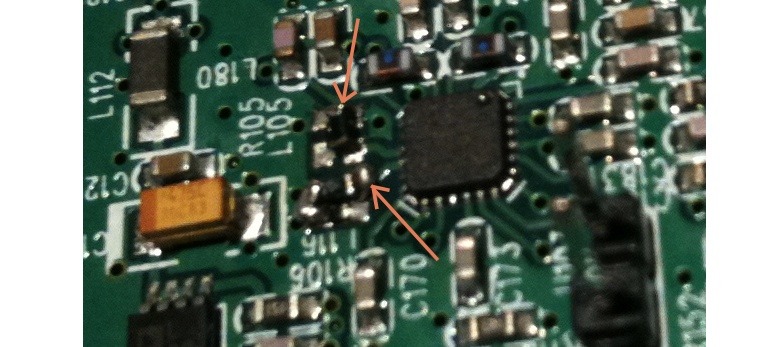
If you try to use this card under 400 Mhz you need at least to change the inductances value from the PLL vco. (He won't lock outside the original band) According to the chip data-sheet the correct value to go on the band III is around 22 nH. Locate the TX PLL:
Then replace the L105 and L115 inductance (in // with R105 and R106)